Custom Data (Apple)
Among the Apple devices, you can collect custom data only for macOS devices, and display the data on the Device Details tab in the Device Information panel. Use the Custom Data dialog box to create, modify, or delete custom data items.
| Override Settings Inherited from Parent Group 'device group name' | Turn on to ignore settings inherited from parent device groups. This option is displayed only in nested device groups. |
| Apply changes to all child groups and devices | Turn on to cascade settings specified here to all nested devices and device groups. |
Turn on Enable Custom Data Configuration.
Custom Data Configuration
The Custom Definitions section lists all the available custom
data items.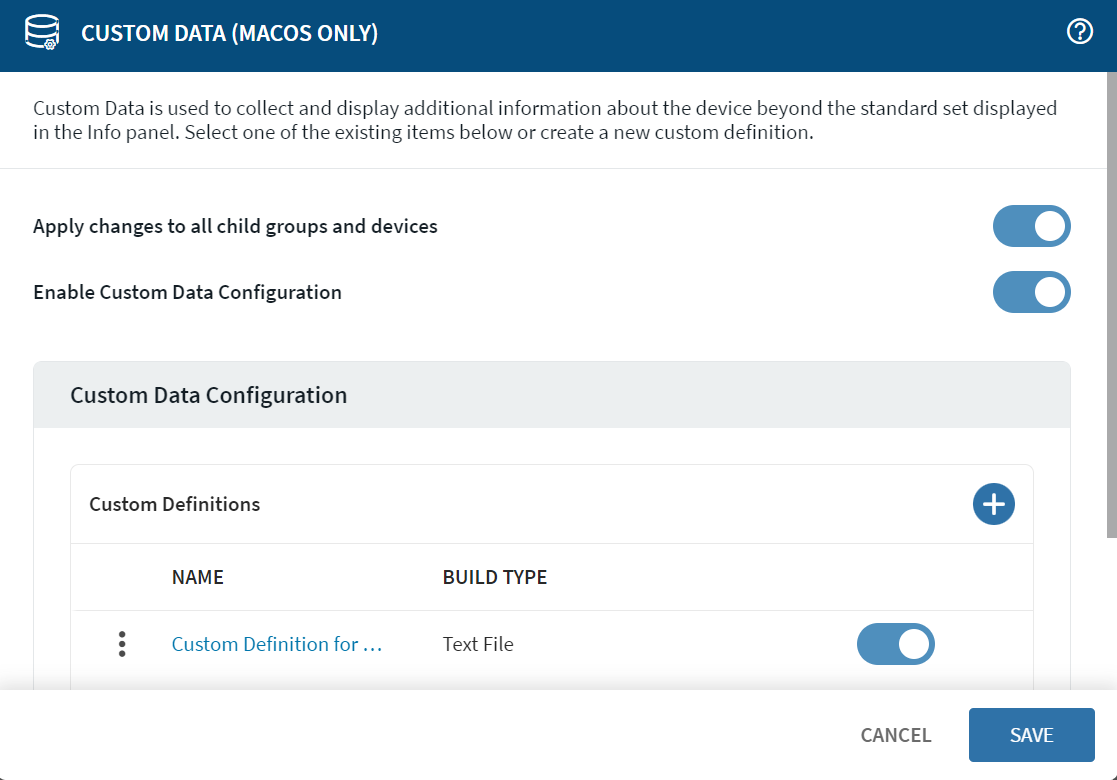
Beside the name of an existing definition, select More to Edit, set Permissions for, or Delete a custom data item.
To add a new custom data definition, select Add. The Definition Info form opens.
Custom Definitions
Use the Definition Info dialog to define new custom data
items.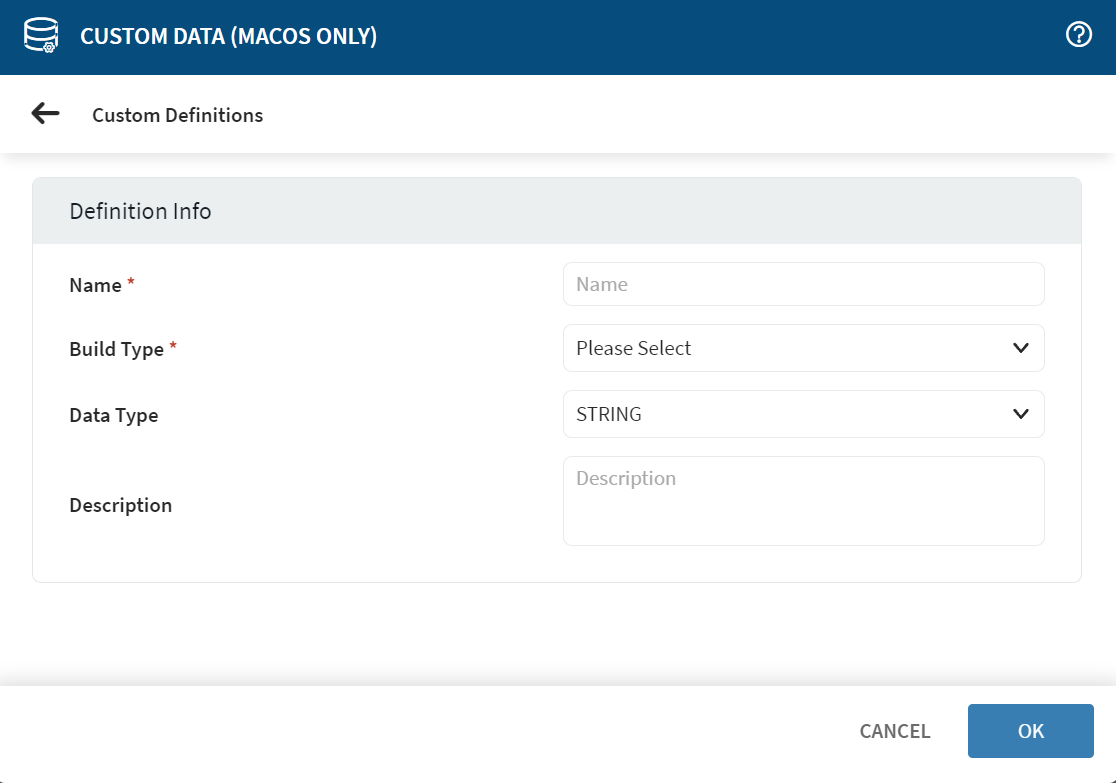
| Name | Enter the name you want to give to this custom data item. This is the display name for the custom data item in the Device Information panel. |
| Build Type | Select a build type for the custom data from the list. MacOS
supports only text file as a Build Type. After you select Text File, the Definition Info section updates to show options specific to your selection. Here, you can define the expression used to extract the custom data from the device. |
| Data Type | The default setting is STRING. Set this field only when collecting custom data. |
| Description | Enter a brief note describing the nature and purpose of the custom data query. |
Build Type: Text File
Displays a line from a text file located on the device.
| Text File | Enter the full path of the text file on the device. |
| Line Number | Enter the line number in the text file. |
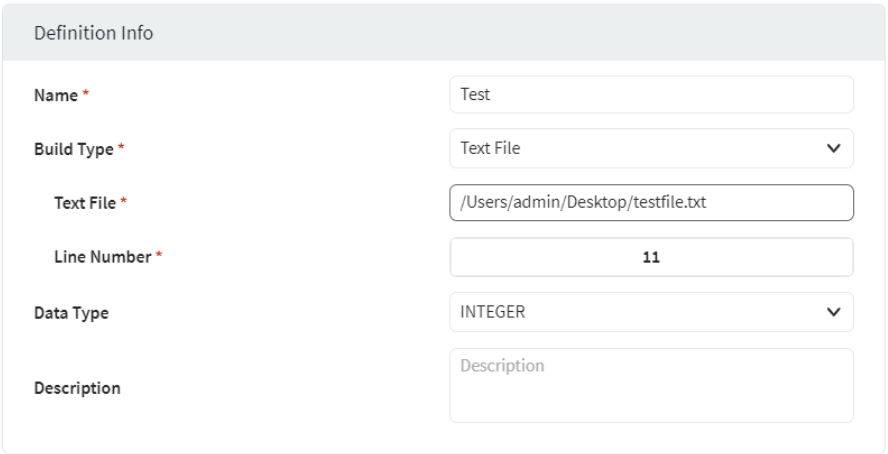
Example:
The following example returns the text from line number eleven of the Text File testfile.txt.
On macOS devices, you can configure the option to read Custom Data from secure locations such as the home directory of a user. For more information, see Security and Privacy.