Custom Data (Windows Modern)
You can collect custom data about a Windows Modern device and display it on the Device Details tab in the Device Information panel. Use the Custom Data dialog box to create, modify, or delete custom data items.
| Override Settings Inherited from Parent Group 'device group name' | Select to ignore settings inherited from parent device groups.
This option only appears on nested device groups. |
| Apply changes to all child groups and devices | Select to cascade settings specified here to all nested devices and device groups. |
Turn on Enable Custom Data Configuration.
Custom Data Configuration
The Custom Definitions section lists all the available custom data items.
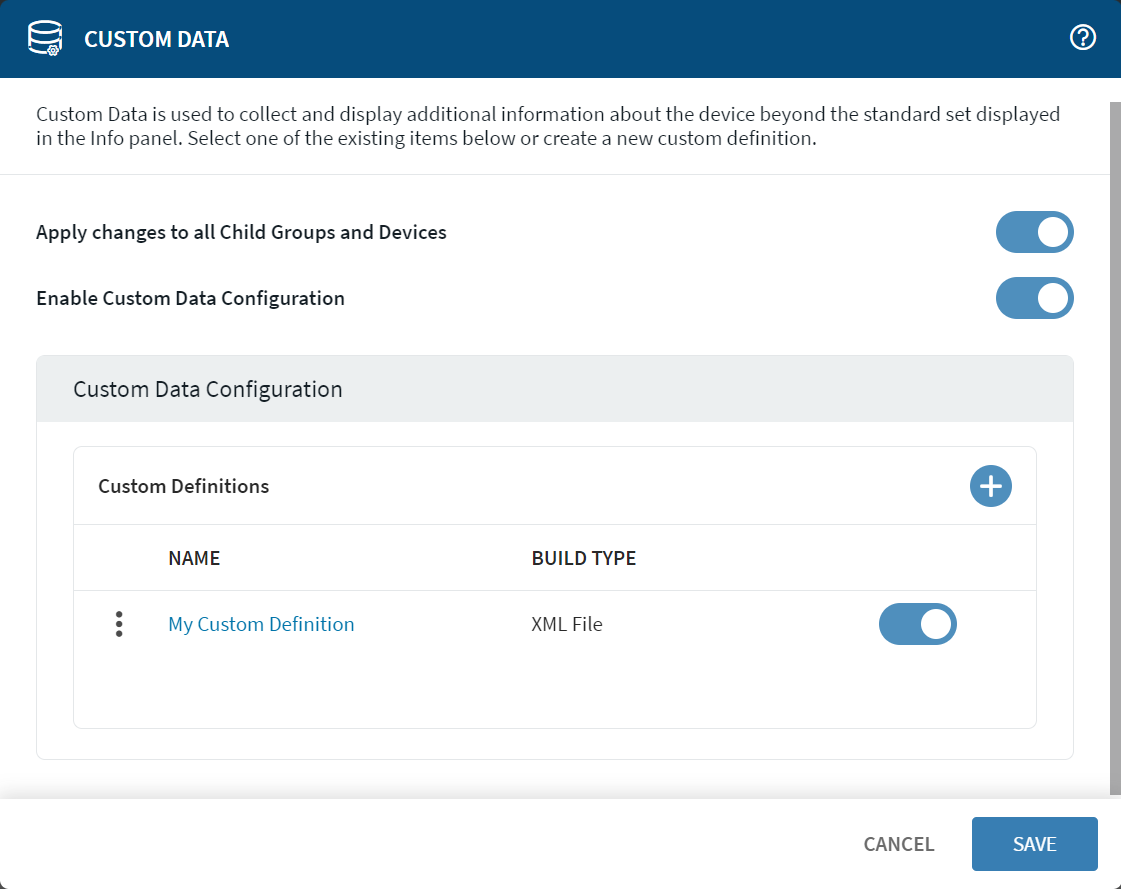
Beside the name of an existing definition, select More to Edit, set Permissions for, or Delete a custom data item.
To add a new custom data definition, select Add. The Definition Info form opens.
Custom Definitions
Use the Definition Info dialog to define new custom data items.
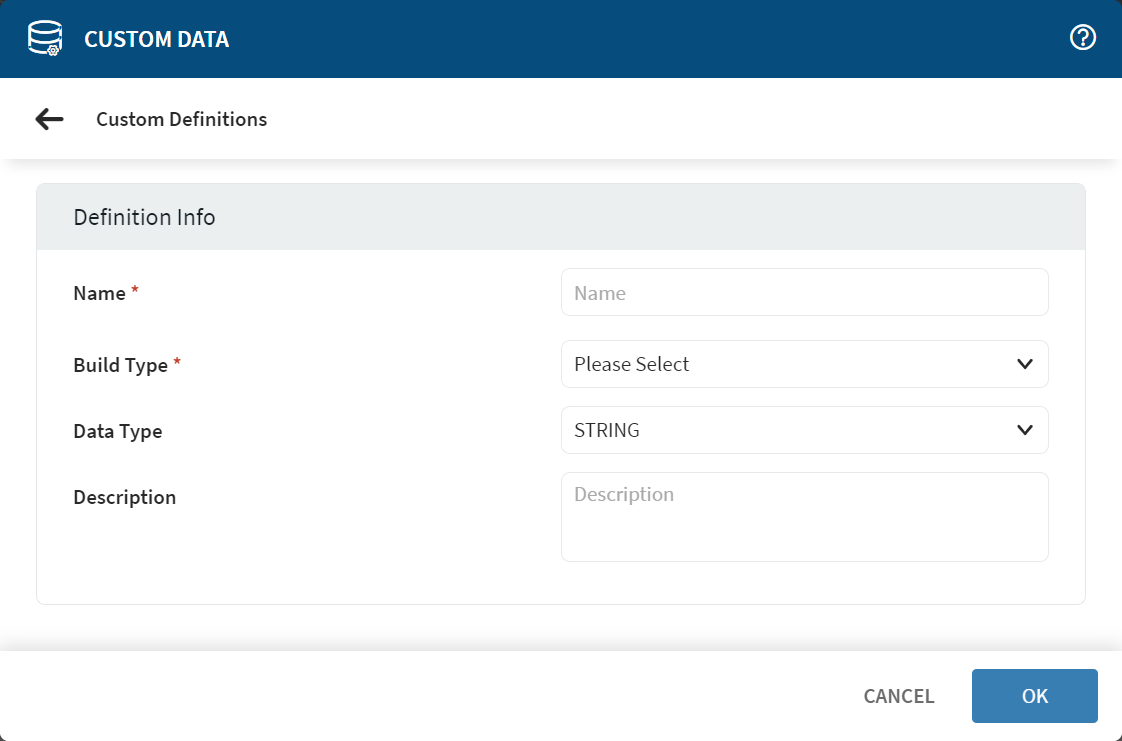
| Name | Enter the name you want to give this custom data item. This is the display name for the custom data item in the Device Information panel. |
| Build Type | Select a build type for the custom data from the list. Once you have selected a build type, the Definition Info section updates to show options specific to your selection. Here, you can define the expression used to extract the custom data from the device. |
| Data Type | The default setting is STRING. Set this field only when collecting custom data. |
| Description | Enter a brief note describing the nature and purpose of the custom data query. |
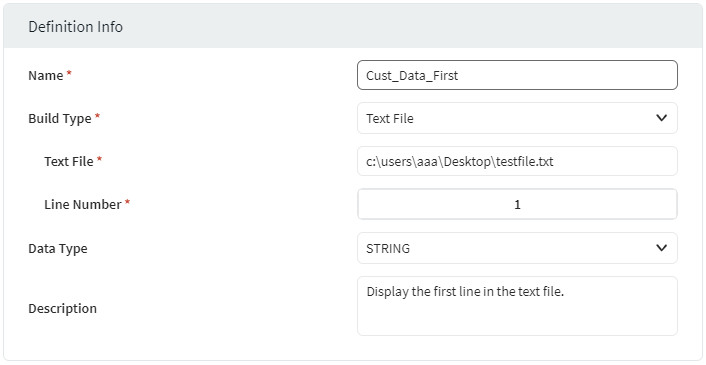
Build Type: Text File
Display a line from a text file located on the device.
| Text File | Enter the full path of the text file on the device. |
| Line Number | Enter the line number in the text file. |
Example:
The following example returns the text from Line Number one of Text File testfile.txt.
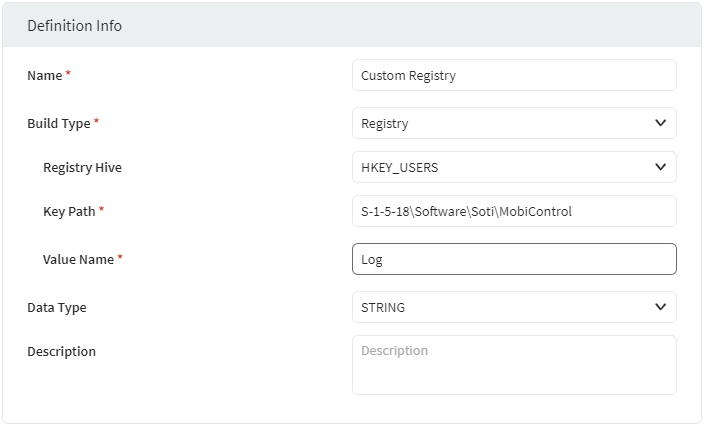
Build Type: Registry
Display a key value from the device's registry.REG_SZ and
REG_DWORD.| Registry Hive | Enter the registry hive. |
| Key Path | Enter the path of the registry key with the value to display. |
| Value Name | Enter the name of the registry value to display. |
The following example returns the registry value for Value Name under the specified Key Path in the named Registry Hive.
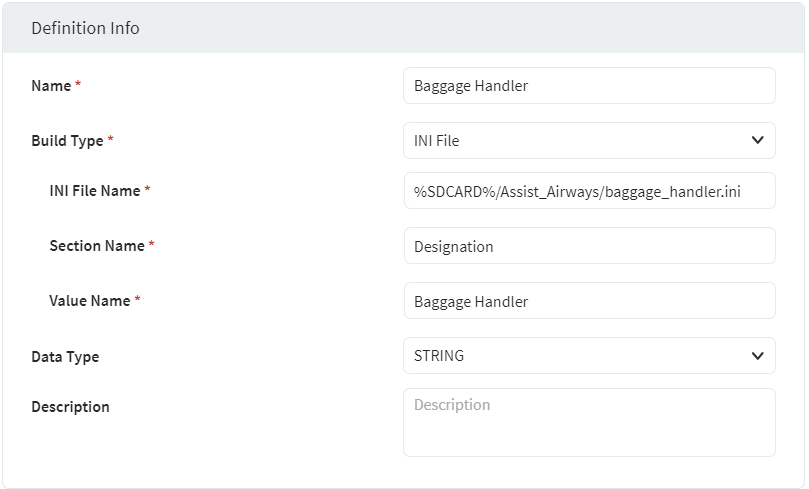
Build Type: INI File
Display the value associated with a given section and property name in an INI file on the device.
| INI File Name | Enter the full path of the INI file on the device. |
| Section Name | Enter the name of the section with the property value to display. |
| Value Name | Enter the property name whose associated value is to display. |
Build Type: Exit Code
Display the exit code returned by an executable program on the device.
| Exit Code | Enter the full path of the executable program on the device whose
exit code you want displayed. If a path is not provided, SOTI MobiControl looks for the program name in default paths, such as C:\WINDOWS\system32. CAUTION: Commands execute with administrator
privileges on the underlying operating system.
Exit codes:
Examples:
|
Build Type: STDOUT
Display the first line of standard output from an executable program on the device.
| STDOUT | Enter the full path of the executable program on the device to
capture the first line of standard output it displays. If a full path to programs such as powershell.exe and cmd.exe is not provided, SOTI MobiControl defaults to the 32-bit versions of those programs. The following examples show STDOUT commands used to invoke 32-bit or 64-bit programs.
|
Build Type: Static
Display information about the device that is statically set. The device has the value assigned rather than pulling it from a device attribute.
| Static | Enter a static value that provides information about the
device. Example: OwnerName="X & Y Corporation, SalesDepartment" |